ad-MED Vitrigel ™ 2
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 is a cell culture insert using a collagen Vitrigel™ membrane as a scaffold for cell culturing. ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 indicates high adhesive property against various kind of animal cells. Also, it is useful for fabrication of three- dimensional tissue models appropriate for drugs and cosmetics development. Recently, it’s considered as a material for MPS devices as well, and it’s a product with high potential.
Vitrigel™ is a registered trademark of National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO).
This product is supported by Agri-Health Translational Research Project from the Ministry of Agriculture,Foresty and Fisheries of Japan.
Collagen Vitrigel™
When the moisture of the collagen gel is removed, the collagen fiber density increases and the collagen gel turns into a film. Because this dehydration process is called “Vitrification”, the film produced by this method is called “Vitrigel™ ”.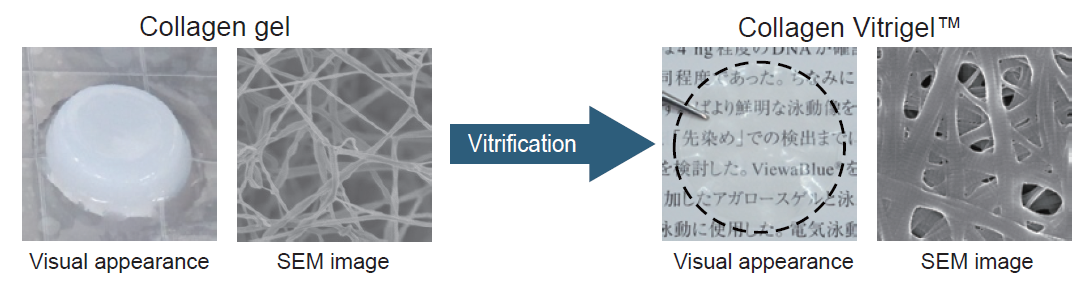
Features

Excellent visibility for observation
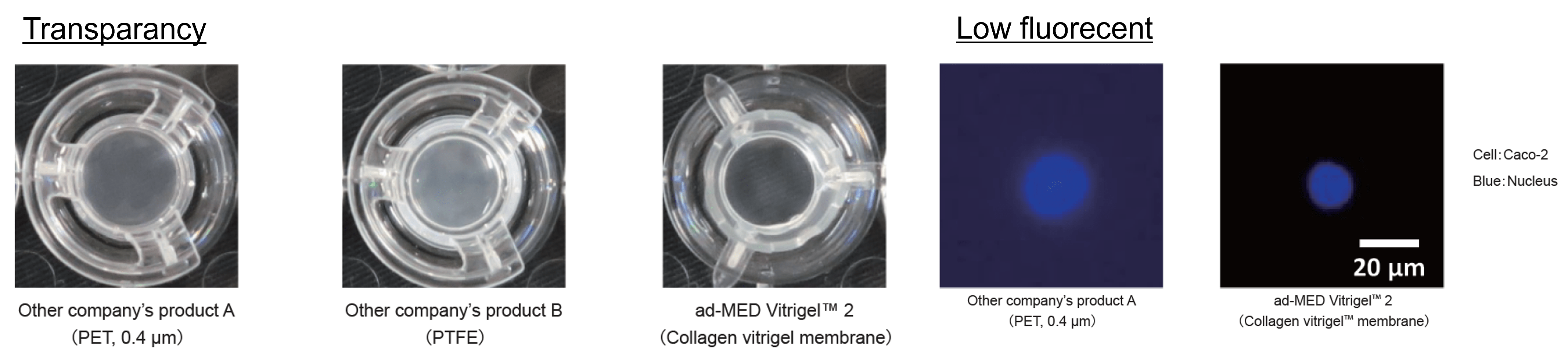
These images indicate transparency of each membranes. Each cell culture inserts were placed on the black cloth after rehydration with PBS. Transparency of collagen Vitrigel™ membrane is higher than that of PET or PTFE membrane. Collagen Vitrigel™ membrane is low fluorescent membrane. It makes high-contrast fluorescent observation.
High adhesive property / Promotion of cell spreading
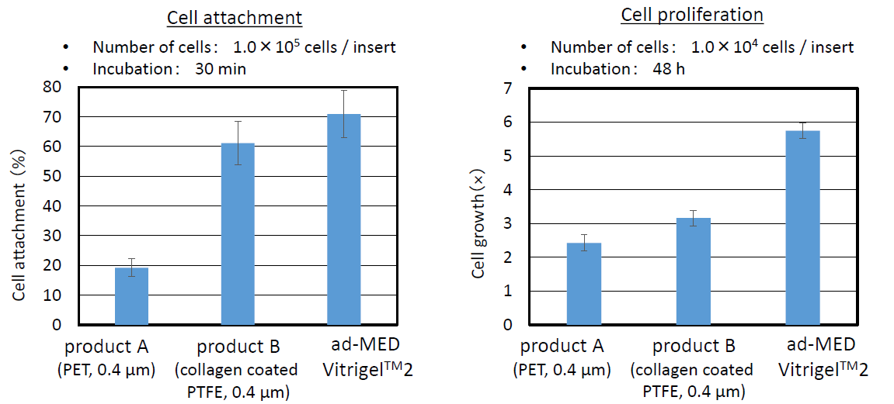
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 indicate excellent cell adhesive property and proliferation acitivity as compare to other cell culture inserts using plastic membrane.
Permeability
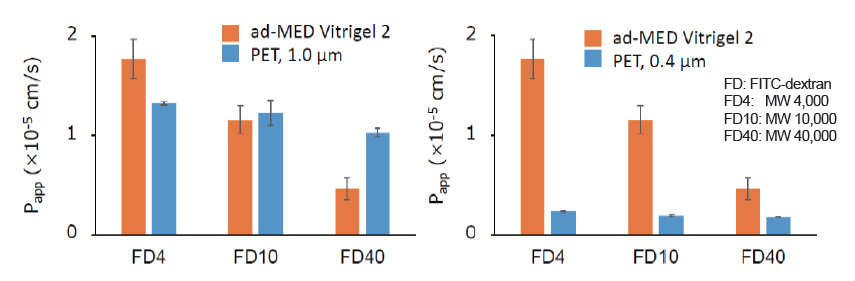
FITC-dextran (MW:4,000 or 10,000 or 40,000) was used as a permeable substance.These results suggested that the permeability of collagen vitrigel membrane was higher than that of PET (0.4 μm) membrane and dependent on the molecular weight of a substance unlike the PET membrane.
Long-term culture
The Vitrigel™ culture method can maintain CYP metabolic activities for at least 3 weeks.
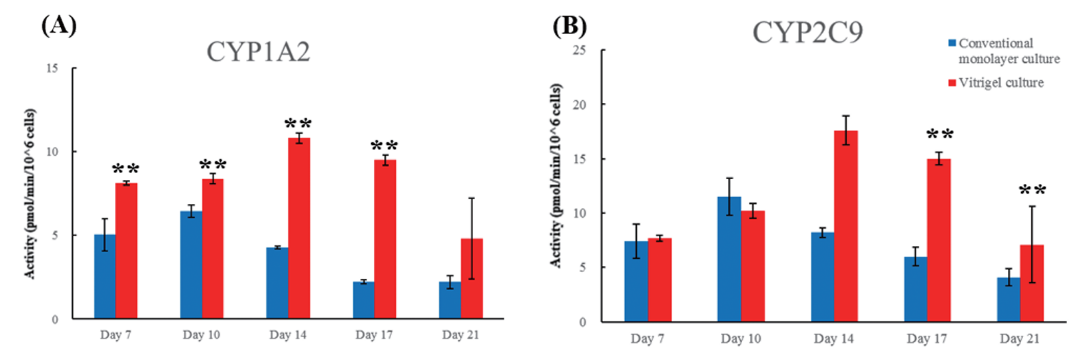
*this data is cited by ChemTime 266 B
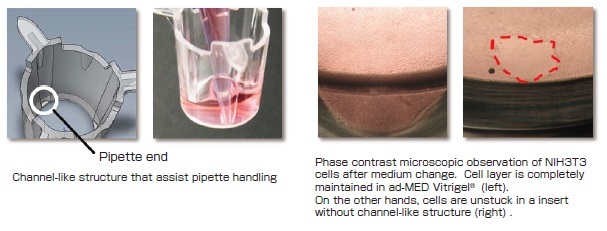
Designs for easier handling
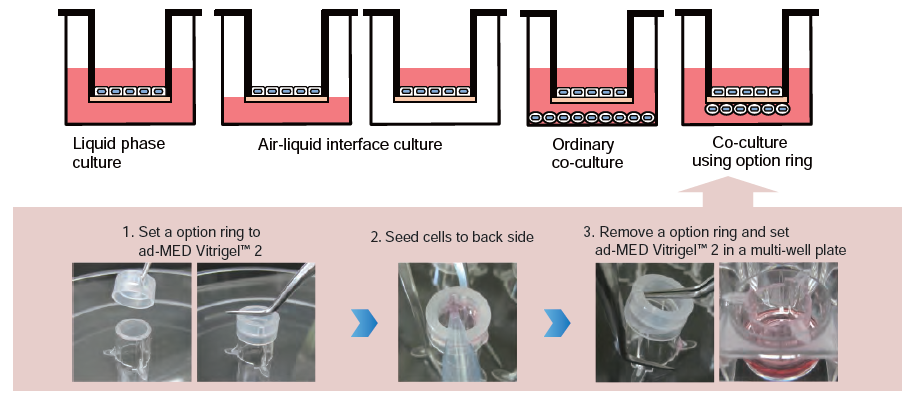
Appropriate for constructing co-culture systems
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 allow to co-culture different type of cells on both inner and outer side of collagen Vitrigel™ membrane by using option ring.
Collagen Vitrigel™ 2 membrane
We also supply Vitrigel™ in processable membrane form in 12 well or 24 well size.
Custom-made products are also available, please contact us.
References
 Intestine
Intestine
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
| hiPSC-intestinal organoids |
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal organoids for pharmacokinetic studies.
Saito T, Amako J, Watanabe T, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Eur J Cell Biol. 2025 Jun;104(2):151489. |
| Caco-2 |
Bridging the gap between in vitro and in vivo solubility-permeability interplay.
Oikawa M, Matsuura S, Okudaira T, Ito R, Arima K, Fushimi M, Oda T, Ohyama K, Kawakami K.
J Pharm Sci. 2025 Jan;114(1):361-370. |
PXB
hiPSC-IECs |
Gut-liver microphysiological systems revealed potential crosstalk mechanism modulating drug metabolism.
Kurniawan DA, Leo S, Inamatsu M, Funaoka S, Aihara T, Aiko M, Rei I, Sakura T, Arakawa H, Kato Y, Matsugi T, Esashika K, Shiraki N, Kume S, Shinha K, Kimura H, Nishikawa M, Sakai Y.
PNAS Nexus. 2024 Feb 9;3(2):pgae070. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
The Effect of Vitamin D3 and Valproic Acid on the Maturation of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Enterocyte-Like Cells.
Leo S, Kato Y, Wu Y, Yokota M, Koike M, Yui S, Tsuchiya K, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Stem Cells. 2023 Aug 16;41(8):775-791. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
Coculture with hiPS-derived intestinal cells enhanced human hepatocyte functions in a pneumatic-pressure-driven two-organ microphysiological system.
Shinohara M, Arakawa H, Oda Y, Shiraki N, Sugiura S, Nishiuchi T, Satoh T, Iino K, Leo S, Kato Y, Araya K, Kawanishi T, Nakatsuji T, Mitsuta M, Inamura K, Goto T, Shinha K, Nihei W, Komori K, Nishikawa M, Kume S, Kato Y, Kanamori T, Sakai Y, Kimura H.
Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 8;11(1):5437. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
Generation of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Functional Enterocyte-Like Cells for Pharmacokinetic Studies.
Yoshida S, Honjo T, Iino K, Ishibe R, Leo S, Shimada T, Watanabe T, Ishikawa M, Maeda K, Kusuhara H, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Feb 9;16(2):295-308. |
 Liver and Cholangiocyte
Liver and Cholangiocyte
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
| HepG2 |
Potential of connexin 32 as a predictive marker for drug-induced cholestatic liver injury in a collagen vitrigel-culture model of HepG2-NIAS cells, a new subline of HepG2 cells, with bile canaliculus-like structures.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
J Toxicol Sci. 2025 |
| HepG2 |
Activation of S1PR2 on macrophages and the hepatocyte S1PR2/RhoA/ROCK1/MLC2 pathway in vanishing bile duct syndrome.
Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Imura T, Takezawa T, Hirai M, Shibata S, Ogi H, Tsujikawa T, Konishi E.
PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0317568. |
| HepG2 |
Modulation of hepatic cellular tight junctions via coculture with cholangiocytes enables non-destructive bile recovery.
Tokito F, Kiyofuji M, Choi H, Nishikawa M, Takezawa T, Sakai Y.
J Biosci Bioeng. 2024 May;137(5):403-411. |
| Cholangiocyte Organoids |
Novel Screening System for Biliary Excretion of Drugs Using Human Cholangiocyte Organoid Monolayers with Directional Drug Transport.
Mizoi K, Okada R, Mashimo A, Masuda N, Itoh M, Ishida S, Yamazaki D, Ogihara T.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(2):427-433. |
| HepG2 |
Novel cell culture technology to harvest hepatic metabolites accumulated in the bile canaliculus-like structures between HepG2-NIAS cells utilizing crosstalk with TFK-1 cells.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
Nano Biomedicine 15.2 (2023): 75-87. |
| hiPSC-hep |
Activation of cAMP (EPAC2) signaling pathway promotes hepatocyte attachment.
Helena GA, Watanabe T, Kato Y, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 31;13(1):12352. |
| HepG2 |
HepG2-NIAS cells, a new subline of HepG2 cells that can enhance not only CYP3A4 activity but also expression of drug transporters and form bile canaliculus-like networks by the oxygenation culture via a collagen vitrigel membrane.
Takezawa T, Uzu M.
J Toxicol Sci. 2022;47(1):39-50. |
| hiPS-hep |
Collagen vitrigel promotes hepatocytic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells.
Nakai S, Shibata I, Shitamichi T, Yamaguchi H, Takagi N, Inoue T, Nakagawa T, Kiyokawa J, Wakabayashi S, Miyoshi T, Higashi E, Ishida S, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Biol Open. 2019 Jul 2;8(7):bio042192. |
| PXB-cells |
Prediction of Human Hepatic Clearance for Cytochrome P450 Substrates via a New Culture Method Using the Collagen Vitrigel Membrane Chamber and Fresh Hepatocytes Isolated from Liver Humanized Mice.
Watari R, Kakiki M, Yamasaki C, Ishida Y, Tateno C, Kuroda Y, Ishida S, Kusano K.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(3):348-353. |
| PXB-cells |
A long-term culture system based on a collagen vitrigel membrane chamber that supports liver-specific functions of hepatocytes isolated from mice with humanized livers.
Watari R, Kakiki M, Oshikata A, Takezawa T, Yamasaki C, Ishida Y, Tateno C, Kuroda Y, Ishida S, Kusano K.
J Toxicol Sci. 2018;43(8):521-529. |
 kidney
kidney
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
| HK-2 |
COMMD5 counteracts cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by maintaining tubular epithelial integrity and autophagy flux.
Ogasawara-Nosoko M, Matsuda H, Ikeda J, Abe M, Masuhiro Y, Endo M, Hamet P, Tremblay J.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):F739-F757. |
 Skin
Skin
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
hASCs
HNDF |
Adipose-derived stromal/stem cells improve epidermal homeostasis.
Moriyama M, Sahara S, Zaiki K, Ueno A, Nakaoji K, Hamada K, Ozawa T, Tsuruta D, Hayakawa T, Moriyama H.
Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 4;9(1):18371. |
| THP‑1 |
Development of a novel in vitro skin sensitization test method using a collagen Vitrigel membrane chamber
Miyazaki H, Yamashita K, Uchino T, Takezawa T, Kojima H.
Alternatives to Animal Testing and Experimentation 22.2 (2017): 141-154. |
 Airway Epithelium
Airway Epithelium
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
| hiPSC-AEC |
An Infection Model for SARS-CoV-2 Using Rat Transplanted with hiPSC-Airway Epithelial Cells.
Kitano M, Ohnishi H, Makino A, Miyamoto T, Hayashi Y, Mizuno K, Kaba S, Kawai Y, Kojima T, Kishimoto Y, Yamamoto N, Tomonaga K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part A. 2025 May;31(9-10):361-372. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Transplantation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia at Different Induction Stages into Nude Rat.
Mizuno K, Ohnishi H, Kishimoto Y, Okuyama H, Kawai Y, Kitano M, Hayashi Y, Omori K.
Cell Reprogram. 2024 Dec;26(6):156-163. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Changes in the Proportion of Each Cell Type After hiPSC-Derived Airway Epithelia Transplantation.
Kitano M, Hayashi Y, Ohnishi H, Okuyama H, Yoshimatsu M, Mizuno K, Kuwata F, Tada T, Kishimoto Y, Morita S, Omori K.
Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241228026. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Comparative Study of Immunodeficient Rat Strains in Engraftment of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia.
Hayashi Y, Ohnishi H, Kitano M, Kishimoto Y, Takezawa T, Okuyama H, Yoshimatsu M, Kuwata F, Tada T, Mizuno K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part A. 2024 Feb;30(3-4):144-153. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Transplantation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia with a Collagen Scaffold into the Nasal Cavity.
Kitada Y, Ohnishi H, Yamamoto N, Kuwata F, Kitano M, Mizuno K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023 Nov;29(11):526-534. |
| hiPSC-MCAC |
Transplantation of multiciliated airway cells derived from human iPS cells using an artificial tracheal patch into rat trachea.
Okuyama H, Ohnishi H, Nakamura R, Yamashita M, Kishimoto Y, Tateya I, Suehiro A, Gotoh S, Takezawa T, Nakamura T, Omori K.
J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Jun;13(6):1019-1030. |
 Placenta
Placenta
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
| TS cells |
Trophoblast stem cell-based organoid models of the human placental barrier.
Hori T, Okae H, Shibata S, Kobayashi N, Kobayashi EH, Oike A, Sekiya A, Arima T, Kaji H.
Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 8;15(1):962. |
 Vascular Endothelium and Cerebral Microvascular Endothelium
Vascular Endothelium and Cerebral Microvascular Endothelium
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
PCNSL
BVP |
Development of a contacting transwell co-culture system for the in vitro propagation of primary central nervous system lymphoma.
Nishi M, Tateishi K, Sundararaj JS, Ino Y, Nakai Y, Hatayama Y, Yamaoka Y, Mihana Y, Miyakawa K, Kimura H, Kimura Y, Yamamoto T, Ryo A.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 27;11:1275519. |
HMEC-1
HDF |
A Hybrid Human Microvascular Endothelial Cell Line Created by Utilizing a Cell Fusion Technique and Its Advantage for Expressing High Endothelial Barrier Function.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
Nano Biomedicine, 14(1), 9-17. |
| HBMEC/ci18 |
Functional analysis of human brain endothelium using a microfluidic device integrating a cell culture insert.
Miura S, Morimoto Y, Furihata T, Takeuchi S.
APL Bioeng. 2022 Mar 9;6(1):016103. |
HUVECs
C2C12 |
Microfluidic system for applying shear flow to endothelial cells on culture insert with collagen vitrigel membrane.
Morimoto Y, Nagata S, Matsumoto M, Sugahara K, Miura S, Takeuchi S.
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 348 (2021): 130675. |
HMVECs
HDM |
Novel microvascular endothelial model utilizing a collagen vitrigel membrane and its advantages for predicting histamine-induced microvascular hyperpermeability.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2020 Nov-Dec;106:106916. |
BECs
pericytes
astrocytes |
Three-dimensional co-culture of blood-brain barrier-composing cells in a culture insert with a collagen vitrigel membrane.
Shima A, Nagata S, Takeuchi S.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020 Aug;56(7):500-504. |
 Others
Others
| Cell Types |
Publication Title |
ihAE
ihAM |
Transplanted artificial amnion membrane enhanced wound healing in third-degree burn injury diabetic mouse model.
Arai K, Yoshida S, Furuichi E, Iwanaga S, Mir TA, Yoshida T.
Regen Ther. 2024 Mar 26;27:170-180. |
MeT-5A
MS-1 |
Fluid dwell impact induces peritoneal fibrosis in the peritoneal cavity reconstructed in vitro.
Aoki S, Noguchi M, Takezawa T, Ikeda S, Uchihashi K, Kuroyama H, Chimuro T, Toda S.
J Artif Organs. 2016 Mar;19(1):87-96. |
MeT-5A
MS-1 |
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and slit function of mesothelial cells are regulated by the cross talk between mesothelial cells and endothelial cells.
Aoki S, Takezawa T, Oshikata-Miyazaki A, Ikeda S, Kuroyama H, Chimuro T, Oguchi Y, Noguchi M, Narisawa Y, Toda S.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;306(1):F116-22. |
Product lineup
| Product No. |
Product Name |
Grade |
Size |
| 08363-96 |
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (12 well) |
for cell culture |
12 pieces/set |
| 08364-96 |
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (24 well) |
for cell culture |
24 pieces/set |
| 08368-96 |
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (96 well) |
for cell culture |
96 well/set |
| 44125-67 |
Vitrigel™ 2 Membrane (φ15 ㎜), sterlie |
for cell culture |
1 pack (24 sheets) |
| 44126-67 |
Vitrigel™ 2 Membrane (φ21 ㎜), sterlie |
for cell culture |
1 pack (24 sheets) |
| 08369-96 |
Option Ring for ad-MED Vitrigel™ (12 well) |
for cell culture |
1 pack (24 pieces) |
| 08373-96 |
Option Ring for ad-MED Vitrigel™ (24 well) |
for cell culture |
1 pack (24 pieces) |
|
Brochure
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 series
Manual
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (12 well)
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (24 well)
ad-MED Vitrigel™ 2 (96 well)










 Intestine
Intestine
 Liver and Cholangiocyte
Liver and Cholangiocyte
 kidney
kidney
 Skin
Skin
 Airway Epithelium
Airway Epithelium
 Placenta
Placenta
 Vascular Endothelium and Cerebral Microvascular Endothelium
Vascular Endothelium and Cerebral Microvascular Endothelium
 Others
Others
