ad-MED ビトリゲル®2
組織再構築に有用なコラーゲンビトリゲル®膜を使用した細胞培養用インサートです。
細胞接着活性・伸展活性に優れ、様々な細胞に対して良好な細胞培養を可能とします。
「ビトリゲル®」は、国立研究開発法人 農業・食品産業技術総合研究機構による登録商標です。
ad-MED ビトリゲル®は、農林水産省「アグリ・ヘルス実用化研究促進プロジェクト (ビトリゲル)」の支援を受けて、国立研究開発法人 農業・食品産業技術総合研究機構と共同で開発されました。
特長
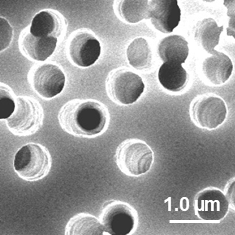
生体結合組織と同等レベルの高密度なコラーゲン繊維構造
ビトリゲル®2膜はコラーゲン繊維が密に絡み合ったメッシュ状の構造を有します。
図:SEMによる表面構造の観察像
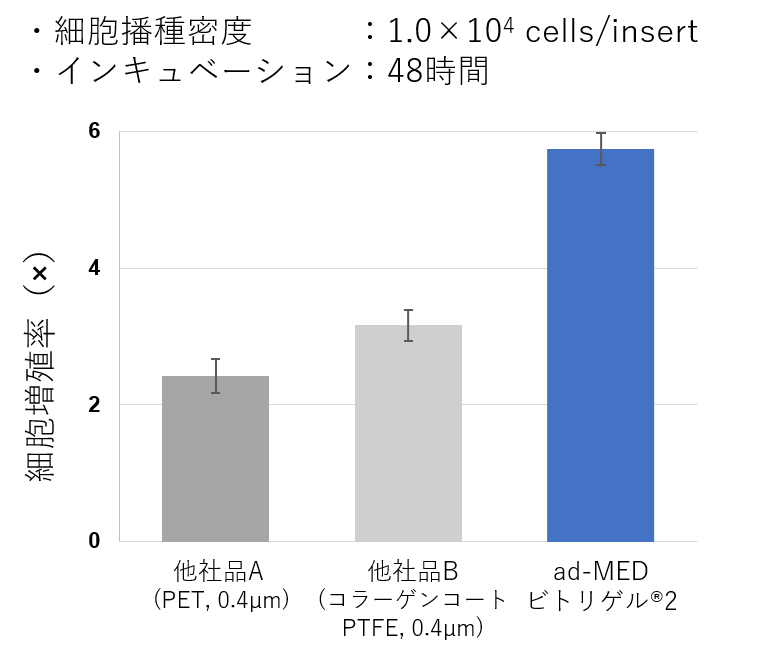
細胞接着性・伸展活性が⾼いコラーゲンビトリゲル®膜
ad-MED ビトリゲル®2は、PET膜やコラーゲンコートPTFE膜を使用したカルチャーインサートと⽐べて細胞の接着性や増殖性が良好です。
図:細胞接着性、細胞増殖性の比較 (Caco-2細胞)
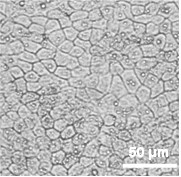
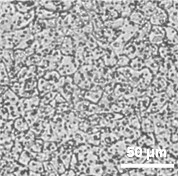
透明性が⾼く、細胞視認性が良好
ビトリゲル®2膜は透明性が高く、細胞の境界を明瞭に観察することができます。
図:細胞培養Day 21 (Caco-2細胞)
⾃家蛍光が低く、免疫染⾊に有⽤
ビトリゲル®2膜は自家蛍光が低いため、バックグランドが上がりにくく、免疫染色時の蛍光シグナルを明瞭に観察することが可能です。
図:細胞核染色時の蛍光観察像 (Caco-2細胞)
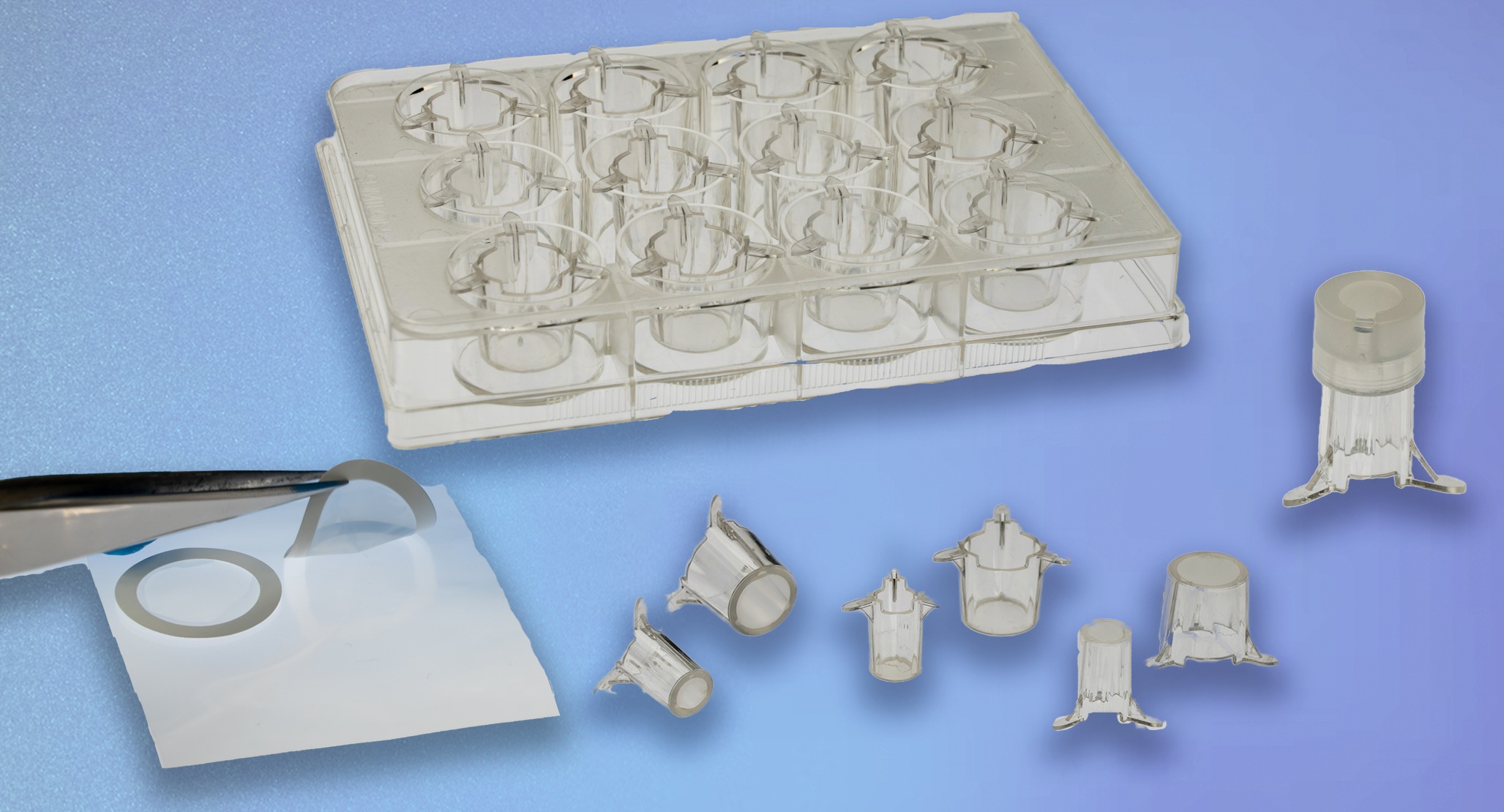
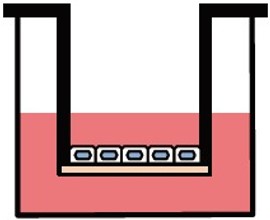
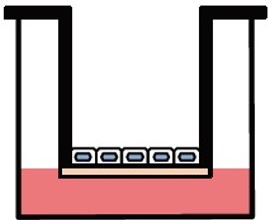
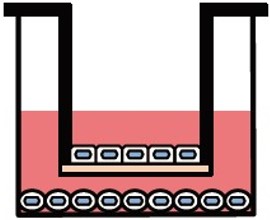
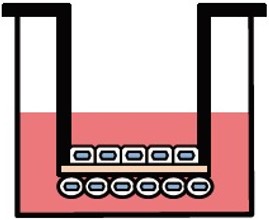
両⾯培養(共培養)による組織モデル構築が可能
ad-MEDビトリゲル®シリーズでは、液相-液相培養、気相-液相培養の他、複数種の細胞種を組み合わせた底⾯・両⾯培養(共培養)が可能で、細胞間相互作⽤解析に有⽤です。
両面培養
別売のオプションリング を装着すると、2種類の異なる細胞をad-MED ビトリゲル®膜の両面に培養することができます。オプションリングはピンセット操作で簡単に脱着できます。
図:ad-MEDビトリゲル®2の外観図 (左)、培養液交換の様子 (右)
論文使用実績
 腸管
腸管
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
| hiPSC-intestinal organoids |
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal organoids for pharmacokinetic studies.
Saito T, Amako J, Watanabe T, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Eur J Cell Biol. 2025 Jun;104(2):151489. |
| Caco-2 |
Bridging the gap between in vitro and in vivo solubility-permeability interplay.
Oikawa M, Matsuura S, Okudaira T, Ito R, Arima K, Fushimi M, Oda T, Ohyama K, Kawakami K.
J Pharm Sci. 2025 Jan;114(1):361-370. |
PXB
hiPSC-IECs |
Gut-liver microphysiological systems revealed potential crosstalk mechanism modulating drug metabolism.
Kurniawan DA, Leo S, Inamatsu M, Funaoka S, Aihara T, Aiko M, Rei I, Sakura T, Arakawa H, Kato Y, Matsugi T, Esashika K, Shiraki N, Kume S, Shinha K, Kimura H, Nishikawa M, Sakai Y.
PNAS Nexus. 2024 Feb 9;3(2):pgae070. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
The Effect of Vitamin D3 and Valproic Acid on the Maturation of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Enterocyte-Like Cells.
Leo S, Kato Y, Wu Y, Yokota M, Koike M, Yui S, Tsuchiya K, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Stem Cells. 2023 Aug 16;41(8):775-791. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
Coculture with hiPS-derived intestinal cells enhanced human hepatocyte functions in a pneumatic-pressure-driven two-organ microphysiological system.
Shinohara M, Arakawa H, Oda Y, Shiraki N, Sugiura S, Nishiuchi T, Satoh T, Iino K, Leo S, Kato Y, Araya K, Kawanishi T, Nakatsuji T, Mitsuta M, Inamura K, Goto T, Shinha K, Nihei W, Komori K, Nishikawa M, Kume S, Kato Y, Kanamori T, Sakai Y, Kimura H.
Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 8;11(1):5437. |
| hiPSC-IECs |
Generation of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Functional Enterocyte-Like Cells for Pharmacokinetic Studies.
Yoshida S, Honjo T, Iino K, Ishibe R, Leo S, Shimada T, Watanabe T, Ishikawa M, Maeda K, Kusuhara H, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Feb 9;16(2):295-308. |
 肝臓・胆管
肝臓・胆管
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
| HepG2 |
Potential of connexin 32 as a predictive marker for drug-induced cholestatic liver injury in a collagen vitrigel-culture model of HepG2-NIAS cells, a new subline of HepG2 cells, with bile canaliculus-like structures.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
J Toxicol Sci. 2025 |
| HepG2 |
Activation of S1PR2 on macrophages and the hepatocyte S1PR2/RhoA/ROCK1/MLC2 pathway in vanishing bile duct syndrome.
Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Imura T, Takezawa T, Hirai M, Shibata S, Ogi H, Tsujikawa T, Konishi E.
PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0317568. |
| HepG2 |
Modulation of hepatic cellular tight junctions via coculture with cholangiocytes enables non-destructive bile recovery.
Tokito F, Kiyofuji M, Choi H, Nishikawa M, Takezawa T, Sakai Y.
J Biosci Bioeng. 2024 May;137(5):403-411. |
| Cholangiocyte Organoids |
Novel Screening System for Biliary Excretion of Drugs Using Human Cholangiocyte Organoid Monolayers with Directional Drug Transport.
Mizoi K, Okada R, Mashimo A, Masuda N, Itoh M, Ishida S, Yamazaki D, Ogihara T.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(2):427-433. |
| HepG2 |
Novel cell culture technology to harvest hepatic metabolites accumulated in the bile canaliculus-like structures between HepG2-NIAS cells utilizing crosstalk with TFK-1 cells.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
Nano Biomedicine 15.2 (2023): 75-87. |
| hiPSC-hep |
Activation of cAMP (EPAC2) signaling pathway promotes hepatocyte attachment.
Helena GA, Watanabe T, Kato Y, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 31;13(1):12352. |
| HepG2 |
HepG2-NIAS cells, a new subline of HepG2 cells that can enhance not only CYP3A4 activity but also expression of drug transporters and form bile canaliculus-like networks by the oxygenation culture via a collagen vitrigel membrane.
Takezawa T, Uzu M.
J Toxicol Sci. 2022;47(1):39-50. |
| hiPS-hep |
Collagen vitrigel promotes hepatocytic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells.
Nakai S, Shibata I, Shitamichi T, Yamaguchi H, Takagi N, Inoue T, Nakagawa T, Kiyokawa J, Wakabayashi S, Miyoshi T, Higashi E, Ishida S, Shiraki N, Kume S.
Biol Open. 2019 Jul 2;8(7):bio042192. |
| PXB-cells |
Prediction of Human Hepatic Clearance for Cytochrome P450 Substrates via a New Culture Method Using the Collagen Vitrigel Membrane Chamber and Fresh Hepatocytes Isolated from Liver Humanized Mice.
Watari R, Kakiki M, Yamasaki C, Ishida Y, Tateno C, Kuroda Y, Ishida S, Kusano K.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(3):348-353. |
| PXB-cells |
A long-term culture system based on a collagen vitrigel membrane chamber that supports liver-specific functions of hepatocytes isolated from mice with humanized livers.
Watari R, Kakiki M, Oshikata A, Takezawa T, Yamasaki C, Ishida Y, Tateno C, Kuroda Y, Ishida S, Kusano K.
J Toxicol Sci. 2018;43(8):521-529. |
 腎臓
腎臓
 皮膚
皮膚
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
hASCs
HNDF |
Adipose-derived stromal/stem cells improve epidermal homeostasis.
Moriyama M, Sahara S, Zaiki K, Ueno A, Nakaoji K, Hamada K, Ozawa T, Tsuruta D, Hayakawa T, Moriyama H.
Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 4;9(1):18371. |
| THP‑1 |
Development of a novel in vitro skin sensitization test method using a collagen Vitrigel membrane chamber
Miyazaki H, Yamashita K, Uchino T, Takezawa T, Kojima H.
Alternatives to Animal Testing and Experimentation 22.2 (2017): 141-154. |
 気道上皮
気道上皮
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
| hiPSC-AEC |
An Infection Model for SARS-CoV-2 Using Rat Transplanted with hiPSC-Airway Epithelial Cells.
Kitano M, Ohnishi H, Makino A, Miyamoto T, Hayashi Y, Mizuno K, Kaba S, Kawai Y, Kojima T, Kishimoto Y, Yamamoto N, Tomonaga K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part A. 2025 May;31(9-10):361-372. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Transplantation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia at Different Induction Stages into Nude Rat.
Mizuno K, Ohnishi H, Kishimoto Y, Okuyama H, Kawai Y, Kitano M, Hayashi Y, Omori K.
Cell Reprogram. 2024 Dec;26(6):156-163. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Changes in the Proportion of Each Cell Type After hiPSC-Derived Airway Epithelia Transplantation.
Kitano M, Hayashi Y, Ohnishi H, Okuyama H, Yoshimatsu M, Mizuno K, Kuwata F, Tada T, Kishimoto Y, Morita S, Omori K.
Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Comparative Study of Immunodeficient Rat Strains in Engraftment of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia.
Hayashi Y, Ohnishi H, Kitano M, Kishimoto Y, Takezawa T, Okuyama H, Yoshimatsu M, Kuwata F, Tada T, Mizuno K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part A. 2024 Feb;30(3-4):144-153. |
| hiPSC-AEC |
Transplantation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Airway Epithelia with a Collagen Scaffold into the Nasal Cavity.
Kitada Y, Ohnishi H, Yamamoto N, Kuwata F, Kitano M, Mizuno K, Omori K.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023 Nov;29(11):526-534. |
| hiPSC-MCAC |
Transplantation of multiciliated airway cells derived from human iPS cells using an artificial tracheal patch into rat trachea.
Okuyama H, Ohnishi H, Nakamura R, Yamashita M, Kishimoto Y, Tateya I, Suehiro A, Gotoh S, Takezawa T, Nakamura T, Omori K.
J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Jun;13(6):1019-1030. |
 胎盤
胎盤
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
| TS cells |
Trophoblast stem cell-based organoid models of the human placental barrier.
Hori T, Okae H, Shibata S, Kobayashi N, Kobayashi EH, Oike A, Sekiya A, Arima T, Kaji H.
Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 8;15(1):962. |
 血管内皮・脳微小血管内皮
血管内皮・脳微小血管内皮
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
PCNSL
BVP |
Development of a contacting transwell co-culture system for the in vitro propagation of primary central nervous system lymphoma.
Nishi M, Tateishi K, Sundararaj JS, Ino Y, Nakai Y, Hatayama Y, Yamaoka Y, Mihana Y, Miyakawa K, Kimura H, Kimura Y, Yamamoto T, Ryo A.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 27;11:1275519. |
HMEC-1
HDF |
A Hybrid Human Microvascular Endothelial Cell Line Created by Utilizing a Cell Fusion Technique and Its Advantage for Expressing High Endothelial Barrier Function.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
Nano Biomedicine, 14(1), 9-17. |
| HBMEC/ci18 |
Functional analysis of human brain endothelium using a microfluidic device integrating a cell culture insert.
Miura S, Morimoto Y, Furihata T, Takeuchi S.
APL Bioeng. 2022 Mar 9;6(1):016103. |
HUVECs
C2C12 |
Microfluidic system for applying shear flow to endothelial cells on culture insert with collagen vitrigel membrane.
Morimoto Y, Nagata S, Matsumoto M, Sugahara K, Miura S, Takeuchi S.
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 348 (2021): 130675. |
HMVECs
HDM |
Novel microvascular endothelial model utilizing a collagen vitrigel membrane and its advantages for predicting histamine-induced microvascular hyperpermeability.
Uzu M, Takezawa T.
J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2020 Nov-Dec;106:106916. |
BECs
pericytes
astrocytes |
Three-dimensional co-culture of blood-brain barrier-composing cells in a culture insert with a collagen vitrigel membrane.
Shima A, Nagata S, Takeuchi S.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020 Aug;56(7):500-504. |
 その他
その他
| 細胞種名 |
論文 |
ihAE
ihAM |
Transplanted artificial amnion membrane enhanced wound healing in third-degree burn injury diabetic mouse model.
Arai K, Yoshida S, Furuichi E, Iwanaga S, Mir TA, Yoshida T.
Regen Ther. 2024 Mar 26;27:170-180. |
MeT-5A
MS-1 |
Fluid dwell impact induces peritoneal fibrosis in the peritoneal cavity reconstructed in vitro.
Aoki S, Noguchi M, Takezawa T, Ikeda S, Uchihashi K, Kuroyama H, Chimuro T, Toda S.
J Artif Organs. 2016 Mar;19(1):87-96. |
MeT-5A
MS-1 |
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and slit function of mesothelial cells are regulated by the cross talk between mesothelial cells and endothelial cells.
Aoki S, Takezawa T, Oshikata-Miyazaki A, Ikeda S, Kuroyama H, Chimuro T, Oguchi Y, Noguchi M, Narisawa Y, Toda S.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;306(1):F116-22. |
製品一覧
| 製品名 |
ad-MED
ビトリゲル®2(12ウェル) |
ad-MED
ビトリゲル®2(24ウェル) |
ad-MED
ビトリゲル®2(96ウェル) |
| プレート |
12 well |
24 well |
96 well |
| 膜面積(cm2) |
1.0 |
0.33 |
0.11 |
| インサート形状 |
ハンギングタイプ |
ハンギングタイプ |
8連 ハンギングタイプ |
| 包装形態 |
12ウェル プレート入り |
24ウェル プレート入り |
96ウェル プレート入り |
| 製品番号 |
製品名 |
保存温度 |
規格 |
包装 |
詳細 |
| 08363-96 |
ad-MED ビトリゲル 2(12ウェル) |
冷蔵 |
細胞培養用 |
12個/set |
 |
| 08364-96 |
ad-MED ビトリゲル 2(24ウェル) |
冷蔵 |
細胞培養用 |
24個/set |
 |
| 08368-96 |
ad-MED ビトリゲル 2(96ウェル) |
冷蔵 |
細胞培養用 |
96ウェル/set |
 |
| 08369-96 |
ad-MED ビトリゲル 専用オプションリング(12ウェル用) |
|
細胞培養用 |
1pack(24個) |
 |
| 32448-67 |
ad-MED ビトリゲル 2(96ウェル)用リザーバープレートセット |
|
細胞培養用 |
1set |
 |
・「法律」,「SDS」,「在庫」など詳細情報は、[Cica-Webで確認]ボタンをクリックいただきご確認いただけます。
・試薬のご購入とご使用に際して
関連製品
パンフレット
ad-MED ビトリゲル®シリーズ
取扱説明書
細胞培養用器材 ad-MED ビトリゲル®2 12ウェル
細胞培養用器材 ad-MED ビトリゲル®2 24ウェル
細胞培養用器材 ad-MED ビトリゲル®2 96ウェル


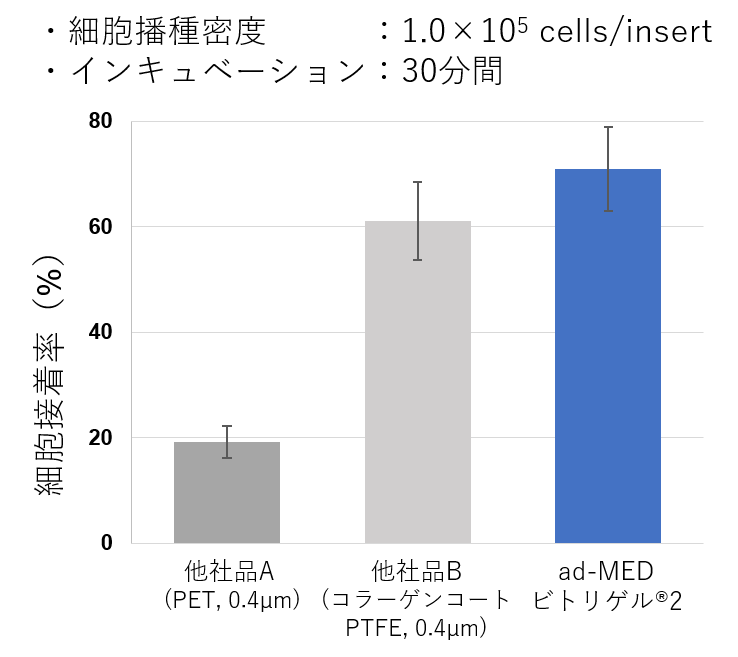






 腸管
腸管
 肝臓・胆管
肝臓・胆管
 腎臓
腎臓
 皮膚
皮膚
 気道上皮
気道上皮
 胎盤
胎盤
 血管内皮・脳微小血管内皮
血管内皮・脳微小血管内皮
 その他
その他



